- 01 Aug 2023
- 8 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
Security Policy
- Updated on 01 Aug 2023
- 8 Minutes to read
- Print
- DarkLight
iNode Security Policy protects the iNode networks by controlling the traffic to and from the networks, and it also controls the traffic between a service running on the iNode and a device behind the iNode within a local network. The security policy contains a list of rules that allow or deny inbound and outbound traffic based on 8-tuple:
- Source/destination network
- Traffic direction
- Source/destination CIDR
- Source/destination port
- Protocol
Each security policy rule consists of the following fields:
- From/To Network — The network from which the traffic originates or the network to which the traffic is destined.
- Traffic Direction - The direction in which the traffic flows within the network. It can be either from a service running in the iNode to a device behind the iNode or from a device behind the iNode to a service running in the iNode. It is applicable only when both source and destination network are specified as local network in a rule.
- Priority — A number from 1 to 65535, inclusive. Security policy rules are processed in priority order; lower numbers have higher priority. Note that only the priority range 1000 to 10000 is available for custom security policy rules; the rest are reserved for Secure Edge internal use.
- Protocol — Protocol of the traffic to match.
- Source/Destination Port — A specific port or a range.
- Source/Destination CIDR — A specific IP address or a CIDR block.
- Action — Allow or Deny the traffic that matches the rule.
The security policy rules are stateful. Thus, if a rule allows traffic to be initiated in one direction, all associated traffic in either direction is allowed.
A default security policy is created for each iNode network. You can customize the iNode network security policy according to your needs by changing specific settings of the iNode network or by creating and applying custom security policies.
The default security policy, the security policy-related network settings, and the custom security policies you apply to the network are aggregated to create one set of security policy rules. This aggregated set of security policy rules is matched against all traffic passing through the iNode network.
Default Security Policy for a WAN Network
Every iNode WAN Network has the following default security policy:
- Inbound:
- (Virtual iNode only) Allow all HTTPS traffic rule, set at high priority. This is required for Secure Edge service to function and you can’t override it.
- Deny all traffic rule, set at the lowest priority. You can override this rule by using a custom policy to allow specific traffic. For example: Allow inbound SSH.
- Outbound:
- Allow all HTTPS traffic rule, set at the highest priority. This is required for Secure Edge service to function and you can’t override it.
- Allow all traffic rule, set at a low priority. You can override this rule by using a custom policy to deny specific traffic. For example: Deny outbound ICMP.
Default Security Policy for a Local Network
Every iNode local network has the following default security policy:
- Inbound:
- Allow all traffic rule, set at a low priority. You can override this rule by using a custom policy to deny specific traffic. For example: Deny inbound ICMP.
- Outbound:
- Deny all traffic between all remote networks via this network, set at a low priority. You can override this rule by changing the network setting Inter Remote Network Traffic. For more information, see Inter-remote Network Traffic.
- Allow all traffic rule, set at a low priority. You can override this rule by using a custom policy to deny specific traffic. For example: Deny outbound ICMP.
Inter-remote Network Traffic
When many Edge iNode networks are connected to one Virtual iNode network, you can allow or deny communication between the Edge iNode networks through the Virtual iNode network. This can be useful to enable or disable site-to-site connectivity using the Virtual iNode network as the hub. By default, the Virtual iNode network is set to deny all traffic between remote networks through this network.
You can change from the default for the Virtual iNode network to allow all traffic between remote networks through this network. Follow these steps:
- From the iNodes > All iNodes page, select the name of the Virtual iNode to display the iNode details page.
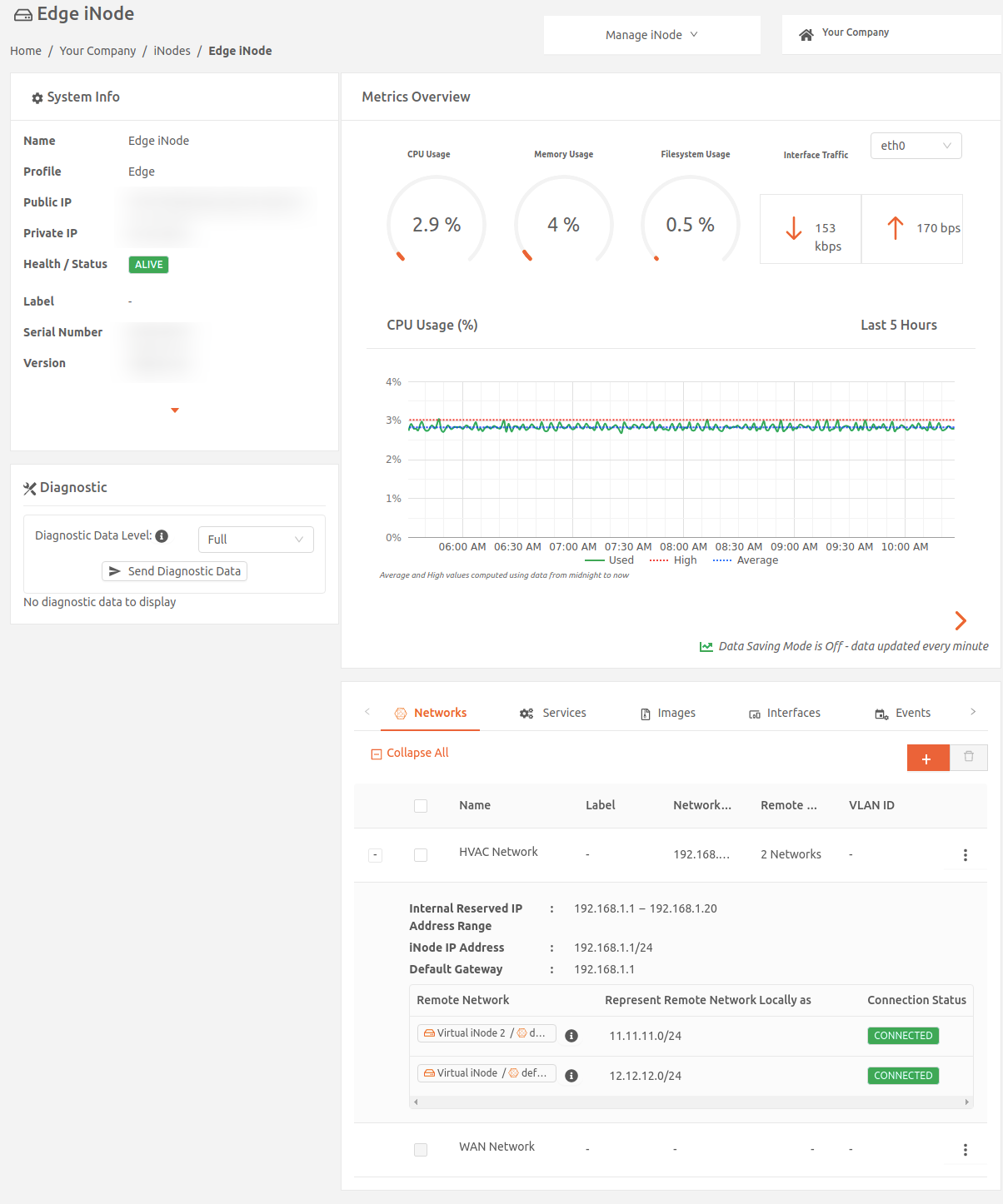
- In the Networks tab, select the name of your local network to display the Edit Network page.
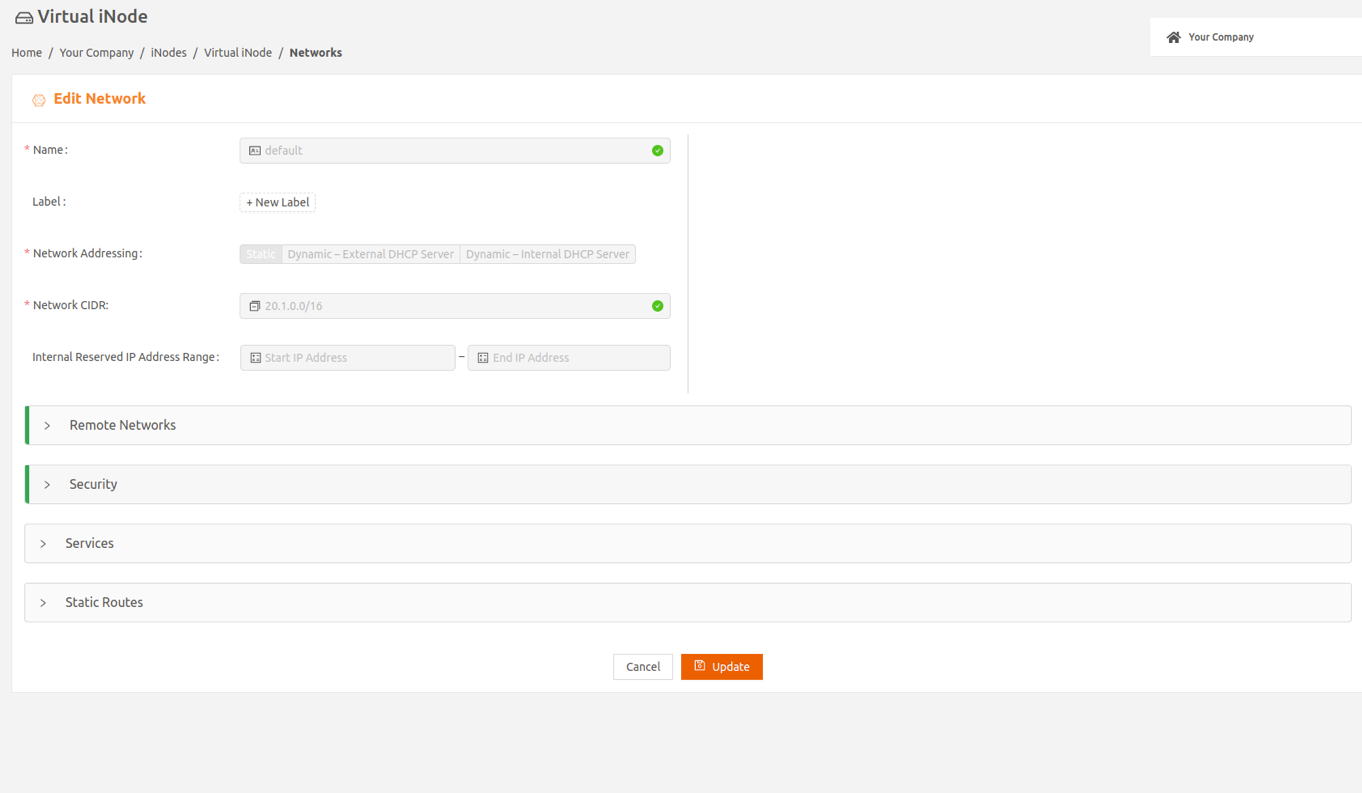
- In the Security expansion panel, change the setting of Inter Remote Network Traffic to Allow.
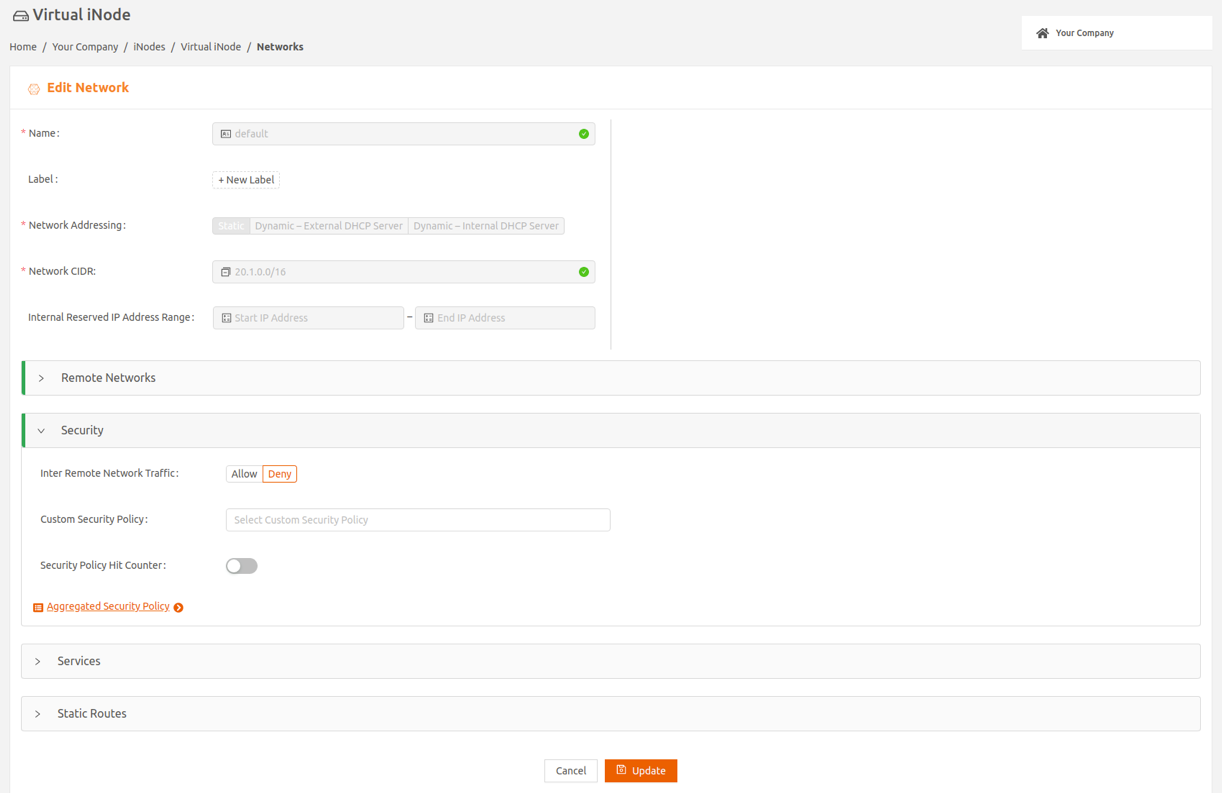
- Confirm this change in the pop-up.
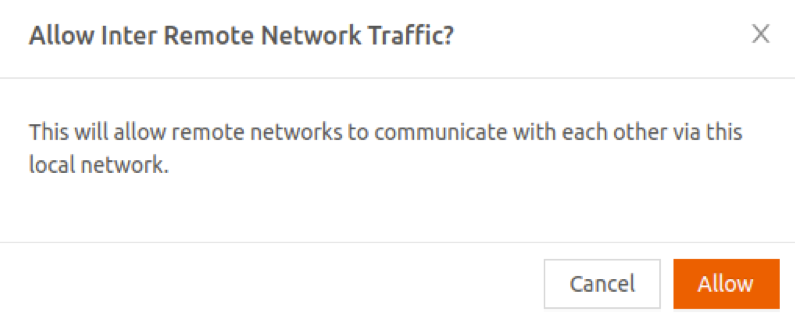
- Select Update for the change to take effect.
Traffic Direction
When you connect a local iNode network to a remote iNode network, you can control the direction in which traffic can be initiated between the two networks. Note that when traffic is allowed to be initiated in one direction, all associated traffic in either direction is allowed. By default, traffic is allowed to be initiated in both directions.
To change from the default to allow traffic to be initiated in a specified direction, follow these steps:
- From the iNodes > All iNodes page, select the name of the Edge iNode to display the iNode details page.
- In the Networks tab, select the name of your local network to display the Edit Network page.
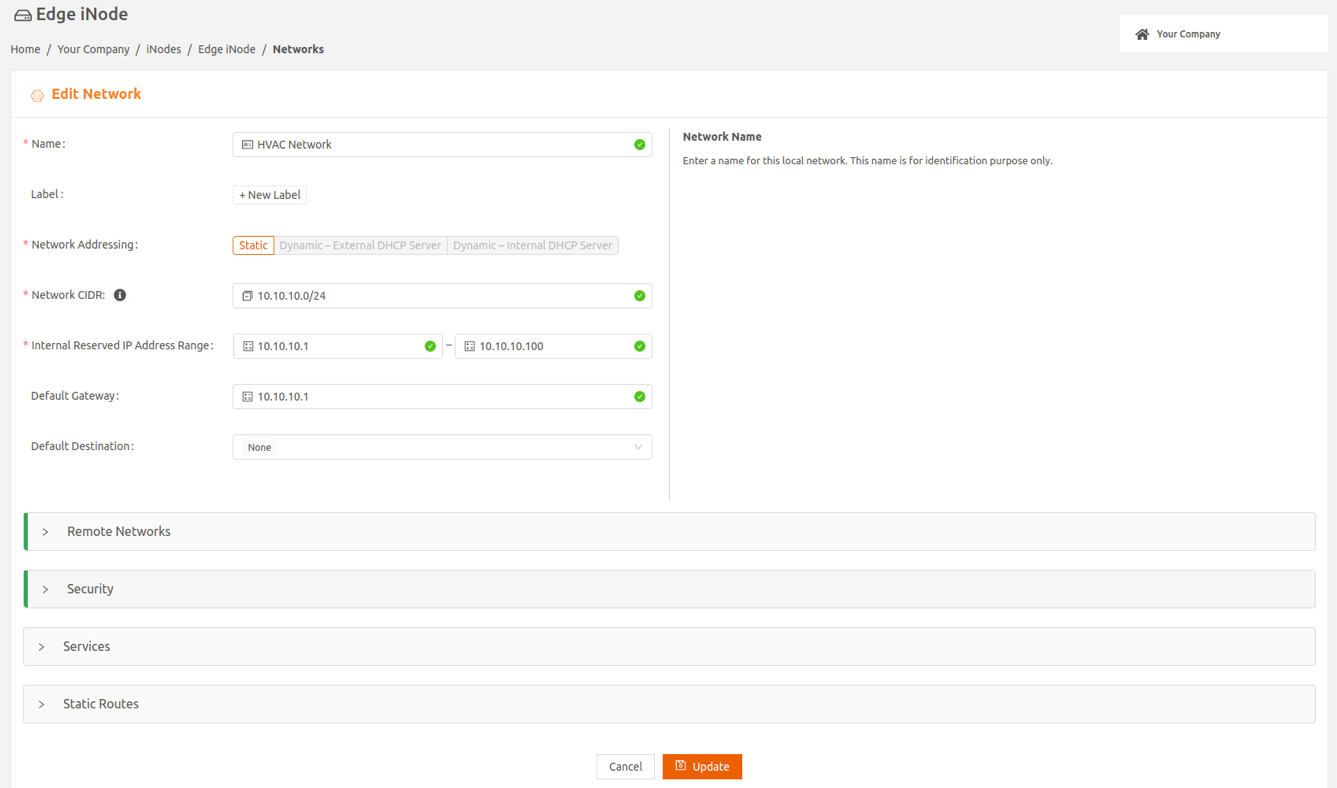
- Select the Remote Networks expansion panel, then select Traffic Direction for the remote network for which you want to change the setting. The remote network row expands to display the choices for Traffic Direction. You can choose to allow:
- Bidirectional (default)
- Local to remote network only, or
- Remote to local network only
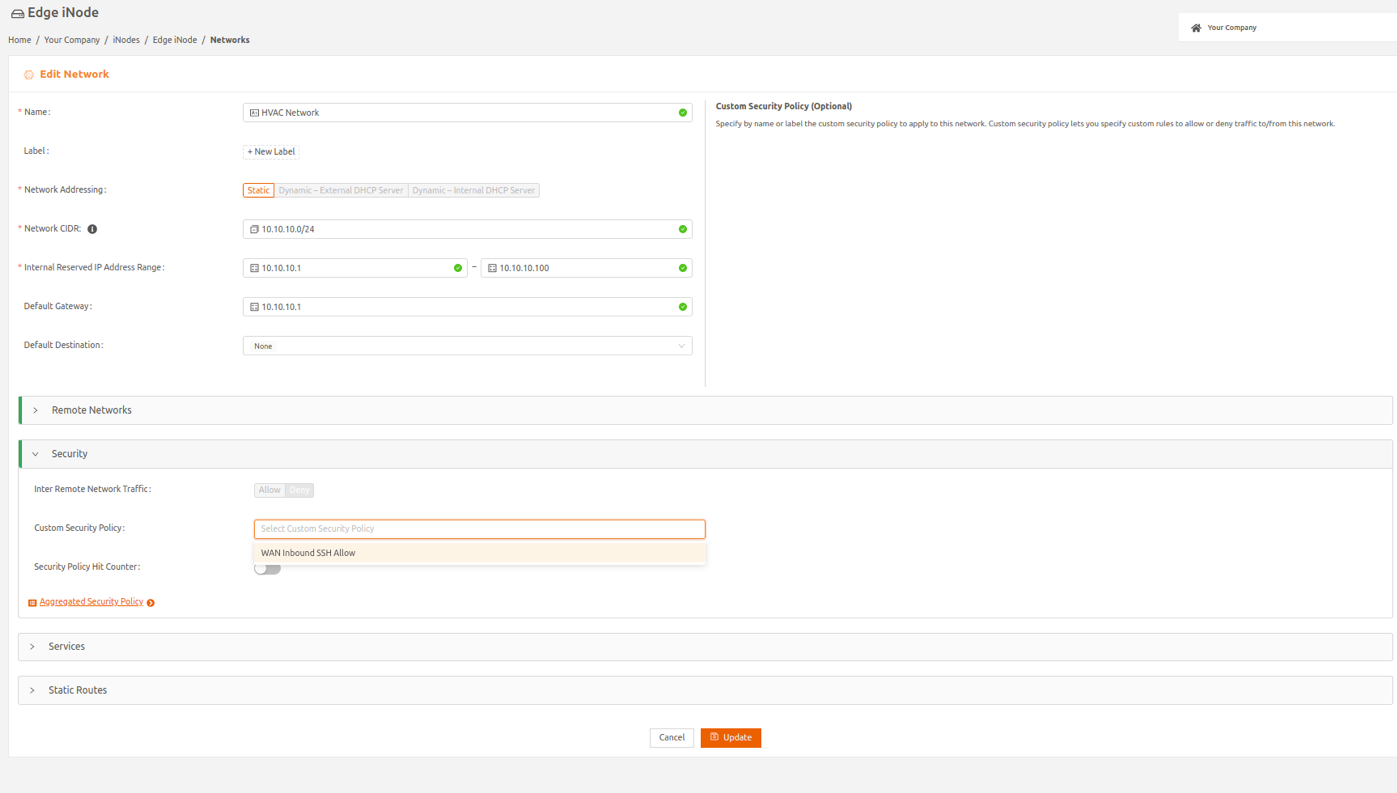
- Select Update for the change to take effect.
Custom Security Policy
A custom security policy allows you to fine-tune control of traffic to and from the iNode networks. To use a custom security policy, you have to define it and then apply it to the desired iNode network.
Adding a Custom Security Policy
To add a custom security policy, follow these steps to define the policy:
- On the Secure Edge Orchestrator left menu, select Networks > Custom Security Policy.
- To add a custom security policy, select the plus sign (+) on the top right.
- Enter a name for the policy and, optionally, specify any custom attribute as Label.
- Under the Rule(s) table, select + Add Rule to add new rules to the table. For each rule, specify the From Network and To Network by name or by label. The default is Any.
- For traffic within the local network, specify From Network and To Network both as local networks (select by name), and choose the Traffic Direction by clicking the appropriate radio button.
- For Priority, specify a number from 1000 to 10000, inclusive.
- Specify rest of the fields (Protocol, Source/Destination Port, Source/Destination CIDR) as needed. The default is Any.
- Select which action to take for the traffic that matches the rule, either Allow or Deny.
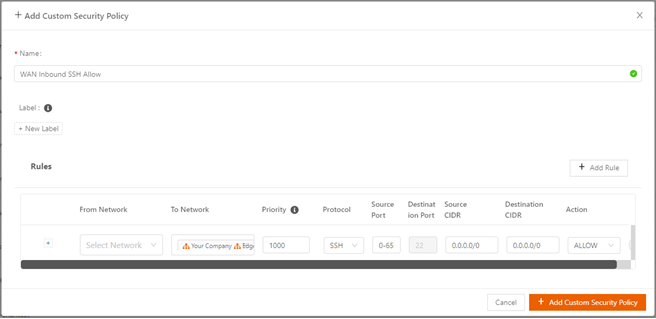
The following screen shows an example for specifying traffic within the local network.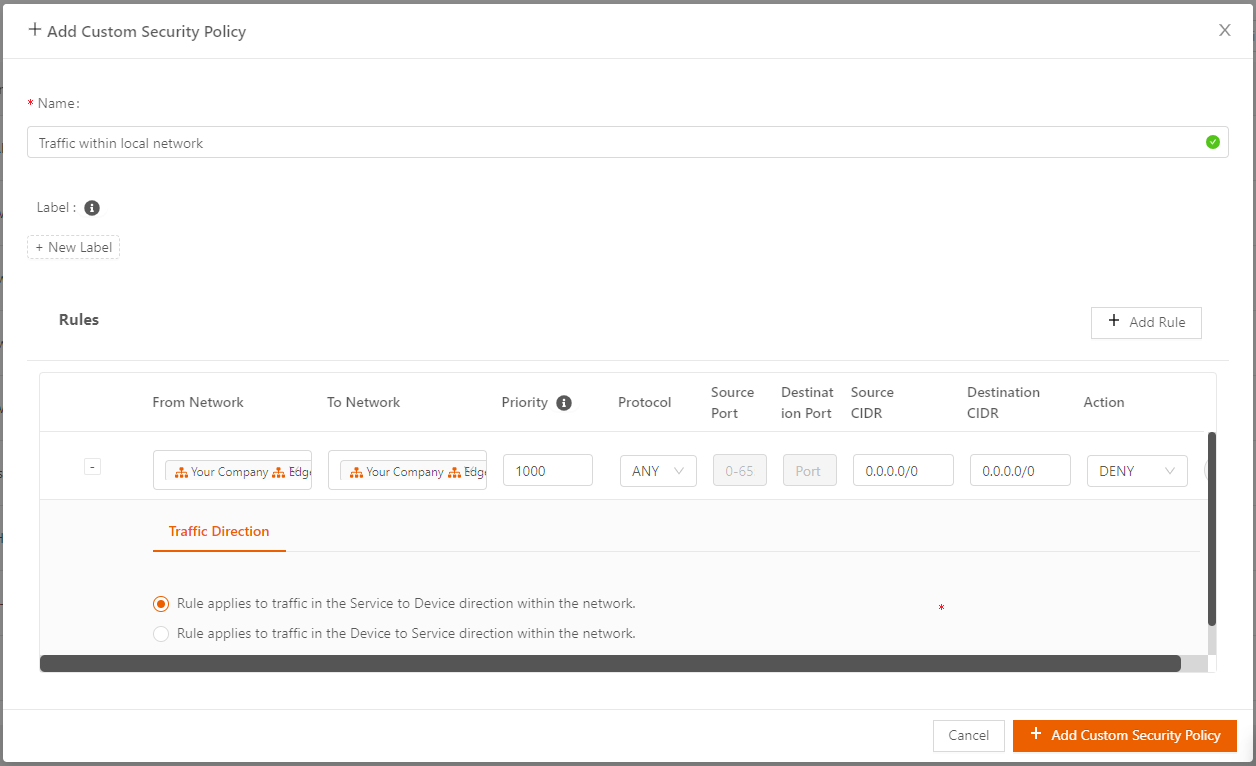
- Select + Add Custom Security Policy to save the policy. The newly added custom policy is listed in the Custom Security Policy screen.

Applying a Custom Security Policy
In the example steps, we’re applying the security policy to a WAN network. To apply the rules in a custom security policy to a network, follow these steps:
- From iNodes > All iNodes, select the name of the Edge iNode to display the iNode details page.

- In the Networks tab, select network to display the Edit Network page.
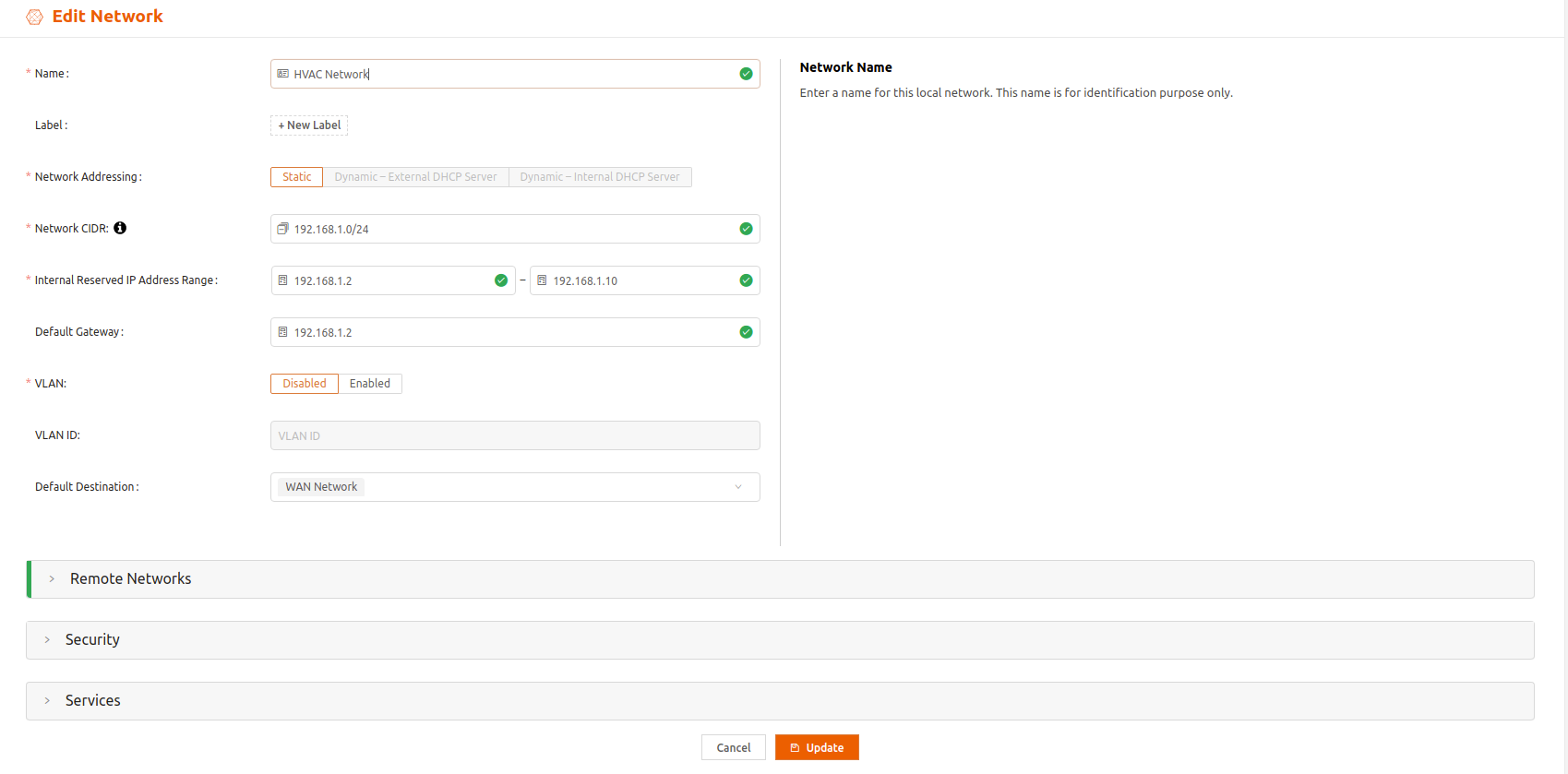
- Select the Security expansion panel. In Custom Security Policy, specify the security policy by name or by label.You can’t apply more than one custom security policy to an iNode network.
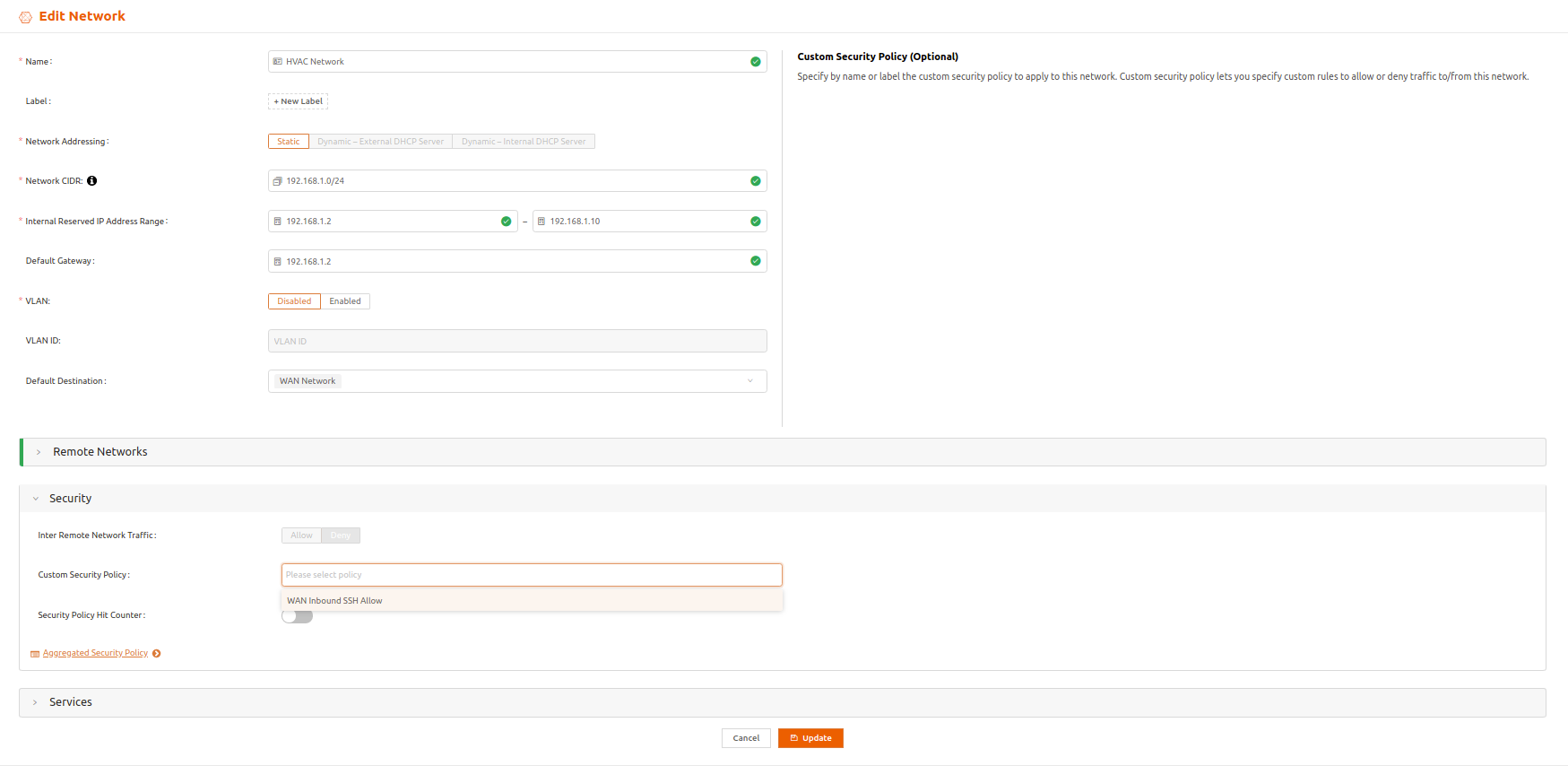
- Select Update for the change to take effect.
Troubleshoot Security Policy Rules
If you find some traffic to or from the iNode network is allowed or denied incorrectly, we offer tools to help you figure out what is going on.
Read on for more information troubleshooting issues with your security policy rules.
Viewing Your Aggregated Security Policy
To look at the complete set of security policy rules being applied to networks in your iNode, follow these steps:
- From iNodes > All iNodes page, select the iNode name to display the iNode details page.
- In the Manage iNode menu, select Aggregated Security Policy. By default, Secure Edge Orchestrator doesn’t display ineffective rules that didn’t resolve to any local or remote network for this iNode. You can change that to show all the rules set by this iNode. To do this, toggle Also show ineffective rules on the top right.
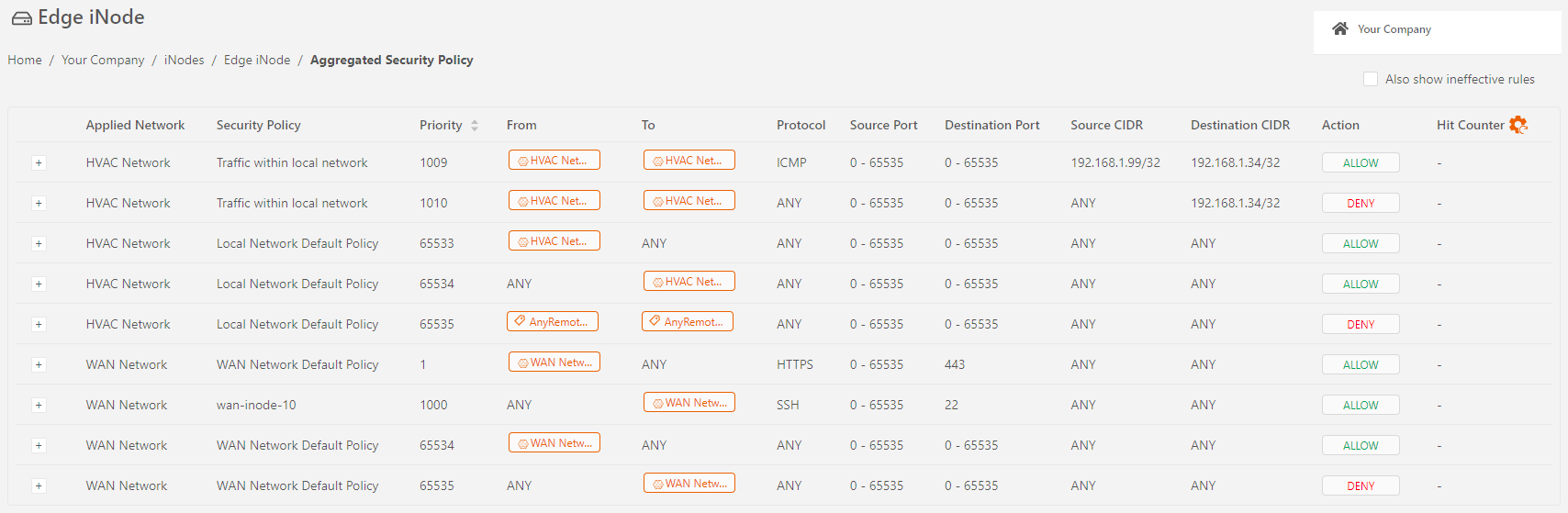
The Aggregate Security Policy display lists the security policy rules in priority order, shows the security policy to which each rule belongs, the network to which each rule is applied, and all the fields of each rule. Also, the list flags ineffective rules and rules with duplicate priority.
You can drill down to view the full set of security policy rules being applied to a particular iNode network. To access the policy rules for an iNode network, follow these steps:
- From iNodes > All iNodes page, select the iNode name to display the iNode details page.
- Select the Security expansion panel.
- Select the Aggregated Security Policy widget.
- Toggle Also show ineffective rules to show all rules set for this network.
To help figure out any issues, you can use this method to review the entire set of security policy rules applied to your each of your iNodes or networks.

Using the Security Policy Hit Counter
Hit counters show the count of packets and bytes that matched each security policy rule. They are useful indicators for packet flows through the iNode network. A hit counter of zero means the rule hasn’t been used, which indicates some other rule with higher priority has matched your traffic. By looking for rules with very high hit count, you could narrow down the rules that are getting hit all the time.
To turn on the hit counter to get information for troubleshooting, follow these steps:
- In the iNode details page for your iNode, under the Networks tab, select the Edit Network icon for the desired network to display the Edit Network page.
- Select the Security expansion panel.
- Toggle the Security Policy Hit Counter.
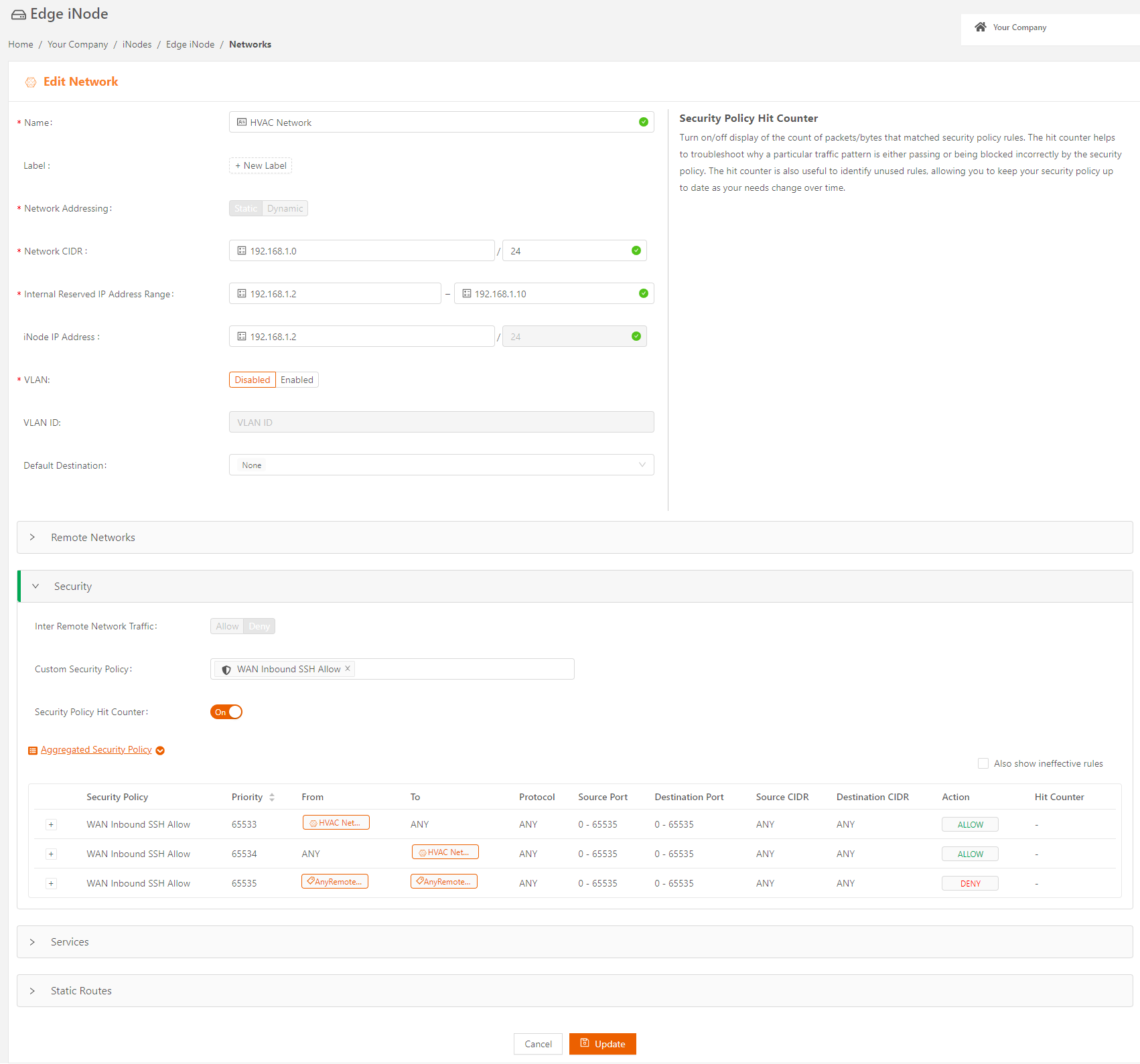
- After up to one minute, review the Aggregated Security Policy. It now displays the count of packets and bytes that matched each security policy rule.
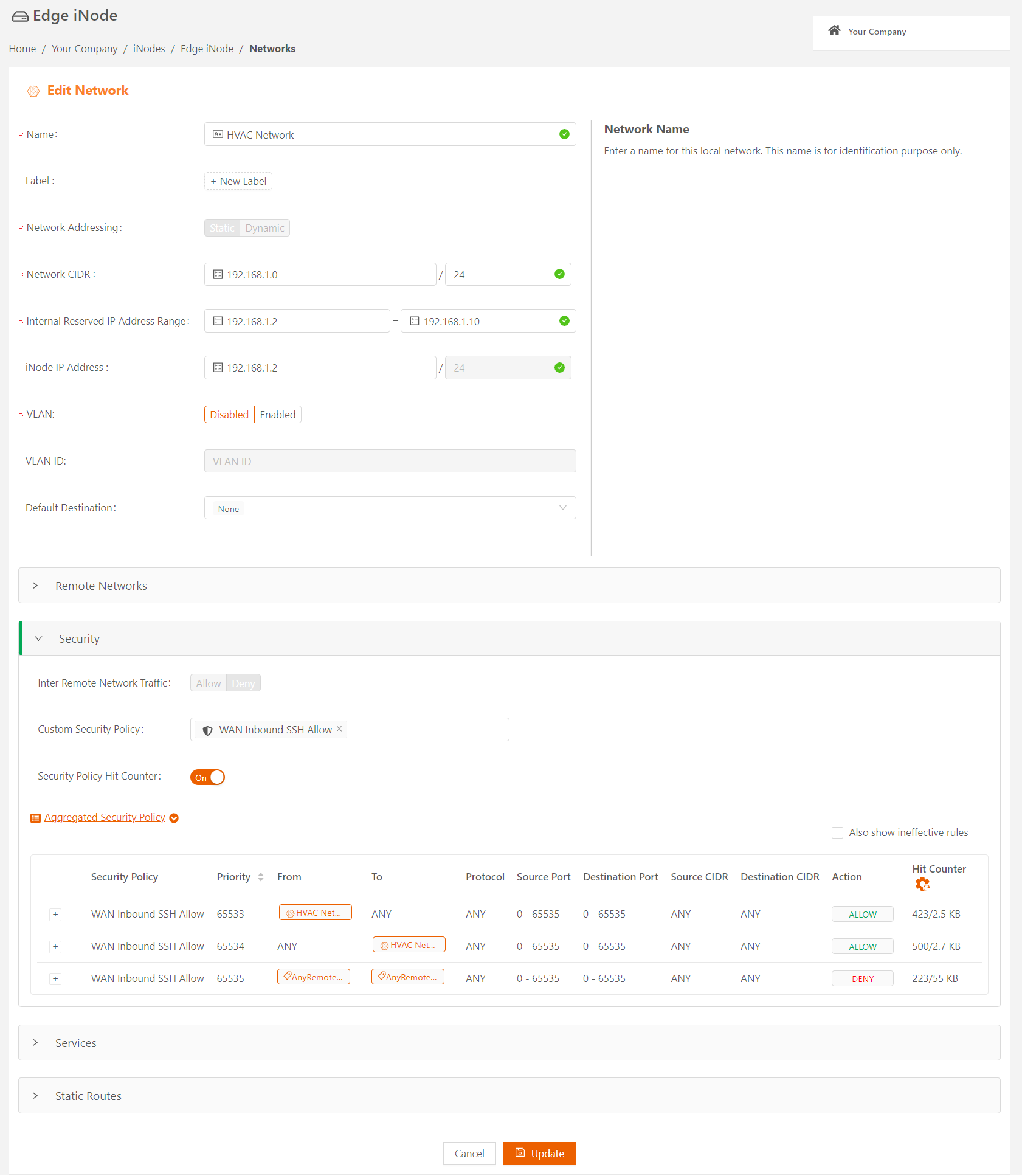
You can also reset the hit counters to gauge the rule usage within a specified period of time. To reset the hit counters, select the icon next to the Hit Counter column. This resets the hit counters for all rules in the network. After up to one minute, view the Aggregated Security Policy. It displays the hit count for each security policy rule after the reset.















